If you have used marijuana in the past, whether it was for medical or recreational use, you have certainly felt the psychoactive effects of the drug. Given the multifaceted nature of marijuana’s effects, it is understandable that there is confusion surrounding its classification as a hallucinogen, stimulant, or depressant, as it has elements of each. To unravel this mystery, a closer look at marijuana’s effects is necessary.
This article will focus on explaining the differences between hallucinogens, stimulants, and depressants, the effects of marijuana, and the risks of marijuana use.

What is Marijuana?
Marijuana, also known as cannabis, weed, bud, or pot, is a psychoactive drug that comes from the leaves, seeds, or stems of the cannabis sativa plant. Marijuana is one of the most commonly used drugs in the United States, with 48.2 million people using it at least once in 2019. The effects of marijuana are a wide range, causing many people to wonder if marijuana is a hallucinogen, stimulant, or depressant.
What are Hallucinogens, Stimulants, and Depressants?
Before we can answer if marijuana is a hallucinogen, stimulant, or depressant, it’s important to understand the differences between the classifications. While many different substances exist worldwide, there are classifications to group together like substances. These classifications are hallucinogens, stimulants, and depressants.
Hallucinogens
Hallucinogens, or psychedelics, can cause psychoactive effects on the body, including altering your perception of reality or inducing hallucinations. This happens due to a change in how your nervous system communicates with your brain. Some common hallucinogens include:
- LSD
- Psilocybin, or magic mushrooms
- Mescaline
- MDMA
Stimulants
Stimulants are substances that increase brain activity, leading to an increase in energy levels, an elevated mood, and enhanced alertness. Stimulants work by increasing the levels of dopamine in your brain, causing euphoric effects throughout the body. Some common stimulants can include:
- Cocaine
- Methamphetamine
- Caffeine
- Amphetamine
Continue reading to learn more about the rehabilitation and risks of meth addiction.
Depressants
Depressants are the opposite of stimulants, slowing down the activity in the brain and the central nervous system. By doing this, they can cause feelings of relaxation and euphoria. While they can produce these calming effects, those who use depressants are at a higher risk of overdose. Some of the most common depressants include:
- Alcohol
- Barbiturates
- Benzodiazepines, such as Xanax
- GHB
Opiates are another form of drug classification that include substances typically used for pain relief. Since these are mostly prescription drugs and due to the opiate effects on the brain, marijuana would not classify as an opioid. Some common opioids are heroin, morphine, and oxycodone.
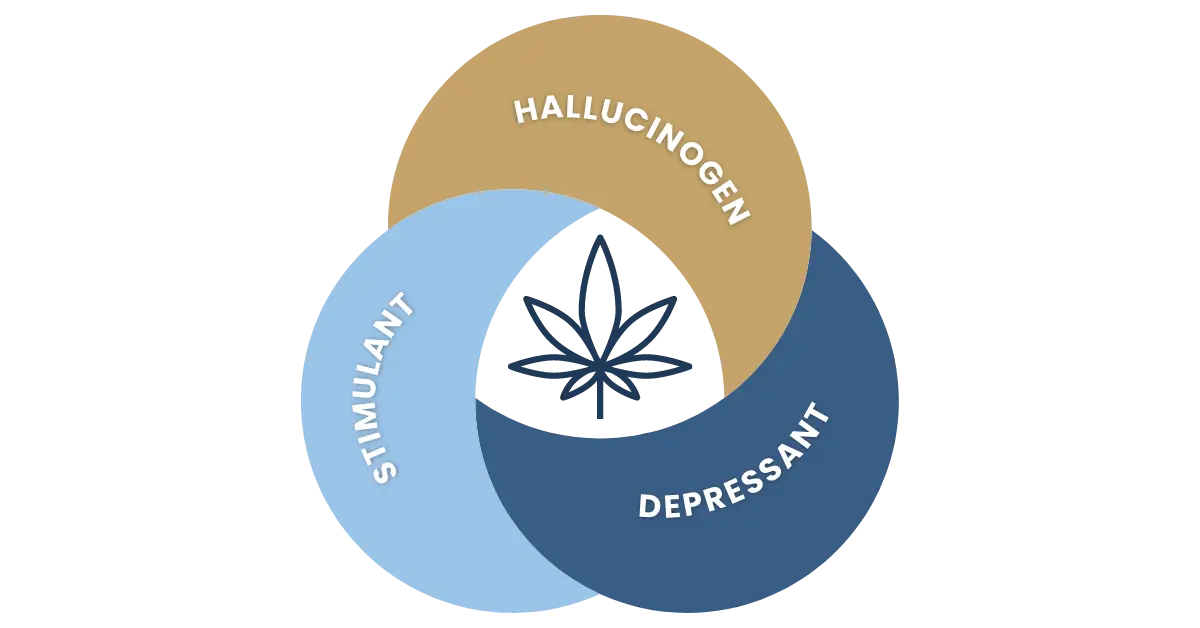
Is Marijuana a Hallucinogen?
Marijuana has the potential to cause symptoms associated with hallucinogens, stimulants, and depressants, making it difficult to classify.
Marijuana’s effects on individuals can vary widely, primarily due to the presence of the main component, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive compound responsible for its mind-altering properties. This causes individuals to experience side effects that can align with hallucinogens, stimulants, and depressants. It’s also important to note that different strains of marijuana can cause different effects on individuals, making it even more difficult to categorize this drug.
To fully answer the question, ‘Is marijuana a hallucinogen?’ we need to discuss the differing effects of marijuana.
Hallucinogenic Effects of Marijuana
As stated previously, marijuana can produce psychoactive and euphoric feelings throughout the body. On top of this, marijuana can also cause hallucinations in some individuals. These hallucinogenic effects are mainly attributed to the presence of THC as it interacts with the cannabinoid receptors in the brain, resulting in a change in sensory perception, cognitive function, and emotion regulation. In addition to these effects, some individuals may experience:
- Dizziness
- Auditory or visual hallucinations
- Tingling sensations throughout the body
- Nausea or vomiting
- Out-of-body experiences
Due to these effects, marijuana is sometimes considered a hallucinogen.
Stimulant Effects of Marijuana
While marijuana is typically associated with sedative effects, it can also cause stimulant effects on specific individuals. This can be attributed to the differing levels of THC and cannabidiol (CBD) in different strains of marijuana. Depending on the strain, individuals may experience more stimulating or depressant effects. Some of the stimulant effects an individual may experience include:
- Increased heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Feelings of paranoia
- Anxiety
- Increased energy levels
Depressant Effects of Marijuana
Marijuana is typically associated with the drug’s depressant effects, making it more likely to be classified as a depressant than any other category. Since marijuana slows down the activity in the brain, many individuals experience similar effects to depressant drugs. Some of these effects include:
- Sleepiness
- Short-term memory loss
- Relaxation
- Reduced inhibitions
- Calmness

The Risks of Marijuana Use
Aside from the effects mentioned above about marijuana use, it’s essential to understand the greater risks of marijuana use. While not considered an addictive substance, long-term use of marijuana can lead to tolerance development, dependency, and withdrawal symptoms. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that in 2020, 3 in 10 people who use marijuana have marijuana use disorder, with the risk of developing this disorder being higher for those in adolescence.
While the use of medical marijuana has grown in popularity throughout the United States, with 38 states approving it for treating mental health conditions and other diseases, there are many risks to be aware of when using marijuana. These risks include:
- Psychosis
- Difficulty in normal brain function
- Delusions
- Impaired motor skills
While marijuana use may be beneficial for some, others may experience the negative effects of marijuana. This kind of unpredictability in a substance requires further research, and those using the substance should proceed with caution. If you or a loved one are struggling with marijuana addiction, it’s crucial to receive treatment to find recovery.
Read more about effective addiction treatment here.
Marijuana Addiction Treatment at East Coast Recovery Center
As mentioned above, marijuana itself is not a highly addictive substance. However, many individuals can still suffer from marijuana addiction or marijuana use disorder. Drug abuse can have devastating effects on an individual’s life, and being addicted to marijuana is no exception.
At East Coast Recovery Center, we offer addiction treatment programs that utilize evidence-based and holistic therapies to provide our clients with the skills, care, and support throughout their recovery. We treat all kinds of drug addiction and understand that every journey is different. Our highly trained medical staff is here to give you individualized treatment plans to fit your unique needs.
If you or a loved one are suffering from marijuana addiction or other drug addictions, contact us today to learn more about our programs. East Coast Recovery is here for you, so we hope you walk the path of recovery with us.
Reviewed By A Specialist In The Field

Vernetta received her Master of Science degree in Clinical Mental Health Counseling at Western Carolina University, and she also holds a MA in History and a BA in Theatre Arts. She is trained in Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) and uses ACT to help clients decrease their suffering and move in the direction of their values. She is passionate about the effectiveness of Experiential Therapy, and has witnessed clients accessing their underlying issues with the aid of creative approaches. She believes in the power and influence of the group process and its ability to propel clients into committed action through the solace of connection. Vernetta is also a HeathRhythms drumming facilitator and enjoys empowering clients to express themselves through rhythm.

Dr. Brady J. Schroer is a psychiatrist in Asheville, North Carolina and is affiliated with Pardee UNC Health Care-Hendersonville. He received his medical degree from Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences College of Osteopathic Medicine and has been in practice for more than 20 years.